Some of the basic fundamental concepts were looked at in a previous blog. If you haven’t had the chance, take a look at it.
We will dig even more profound into vSAN and we’ll see how its components internally interact with each other. First of all, there are certain terminologies that need to be taken into account.
Terminologies
CLOM: Cluster Level Object Manager
DOM: Distributed Object Manager
LSOM: Local Log-Structured Object Manager
CMMDS: Cluster Membership, Monitoring, and Directory Services
RDT: Reliable Datagram Transport
CLOM
This component of vSAN manages and takes care of the overall operations of vSAN cluster and it runs on every host in a cluster. As pointed out earlier in another blogpost, we have objects as a unit of storage that will be stored on vSAN datastore, and storage policies will be applied to these objects. CLOM does the followings:
- It validates whether or not an object should be created to comply with policies.
- It does the creation and migration of objects.
- It load-balances between vSAN nodes.
- It is responsible for proactive and reactive rebalancing.
DOM
DOM also runs on every host in a vSAN cluster. I/O requests are serviced initially through DOM.
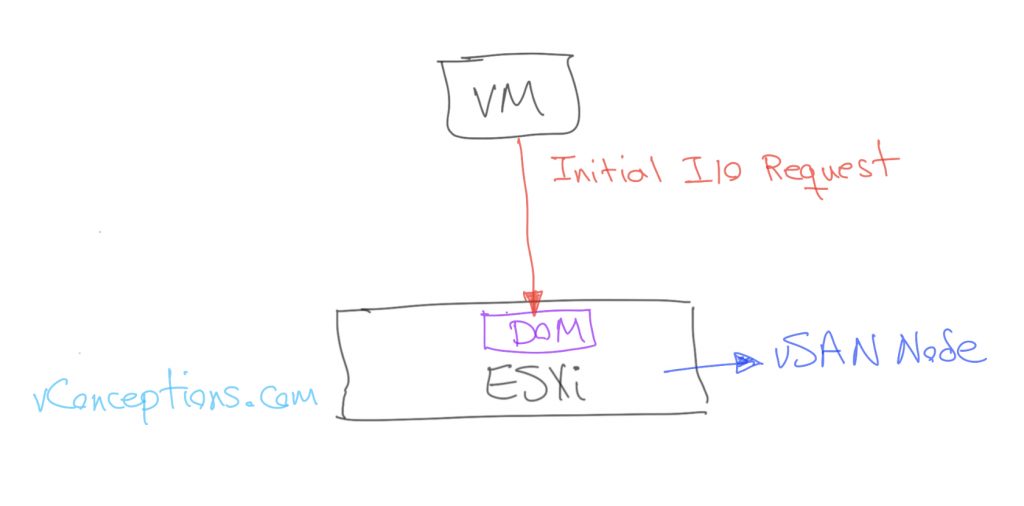
Initial I/O request in a vSAN cluster
It also does the replication of objects. On the other hand, DOM interacts with CLOM and DOMs on other hosts. In other words, CLOM will tell what DOM has to do.

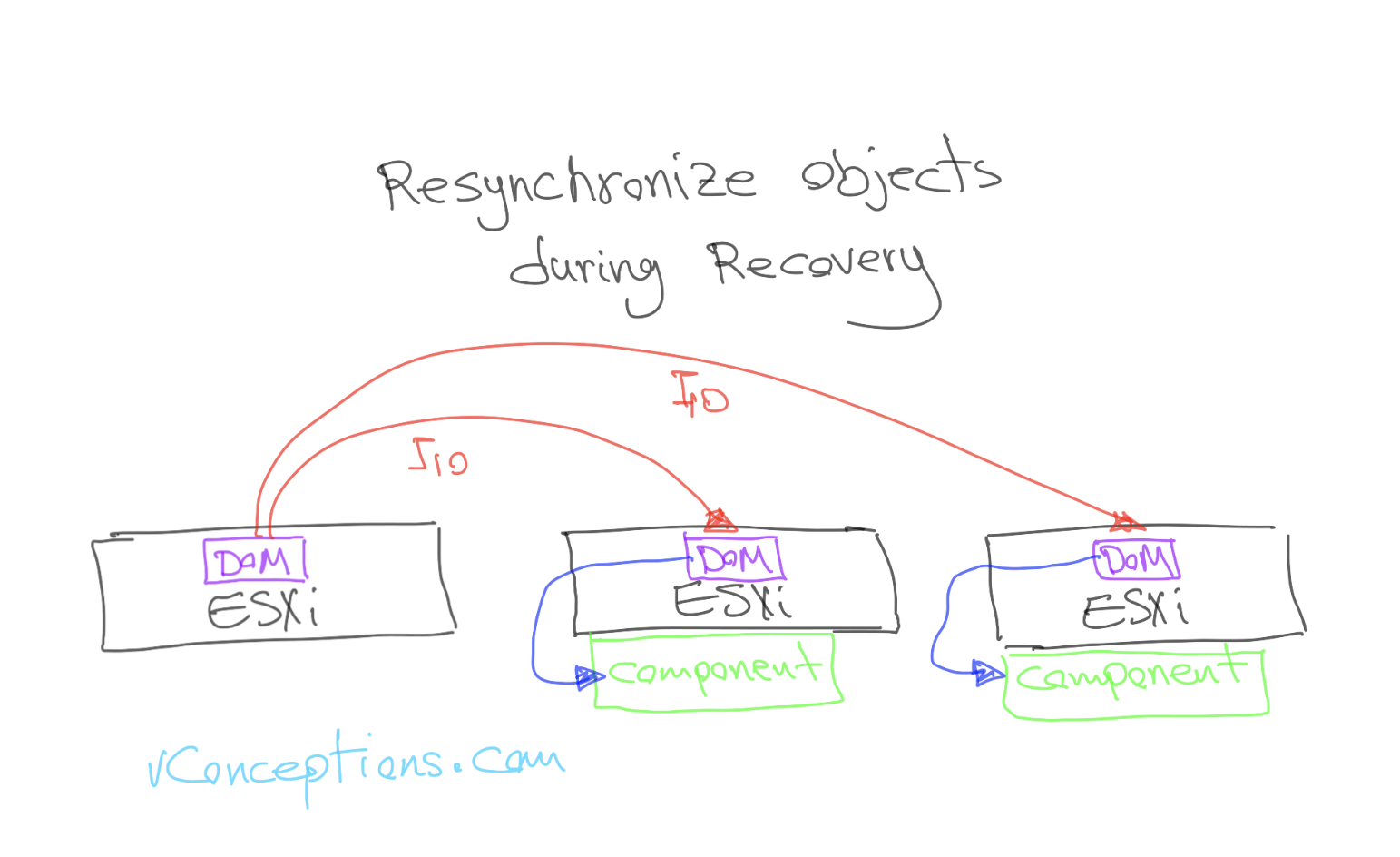
The other important thing that DOM will take care of is telling LSOM to create local components of an object:
- DOM services on all hosts interact with each other to create components.
- during recovery, all DOMs will synchronize objects.

In a vSAN cluster, an object has certain characteristics:
- DOM owner
- DOM client
- DOM component manager
DOM Client: Processes the I/O request sent from the VM, therefore, it will run on every node that has running VMs. It also forwards I/O to the DOM owner.
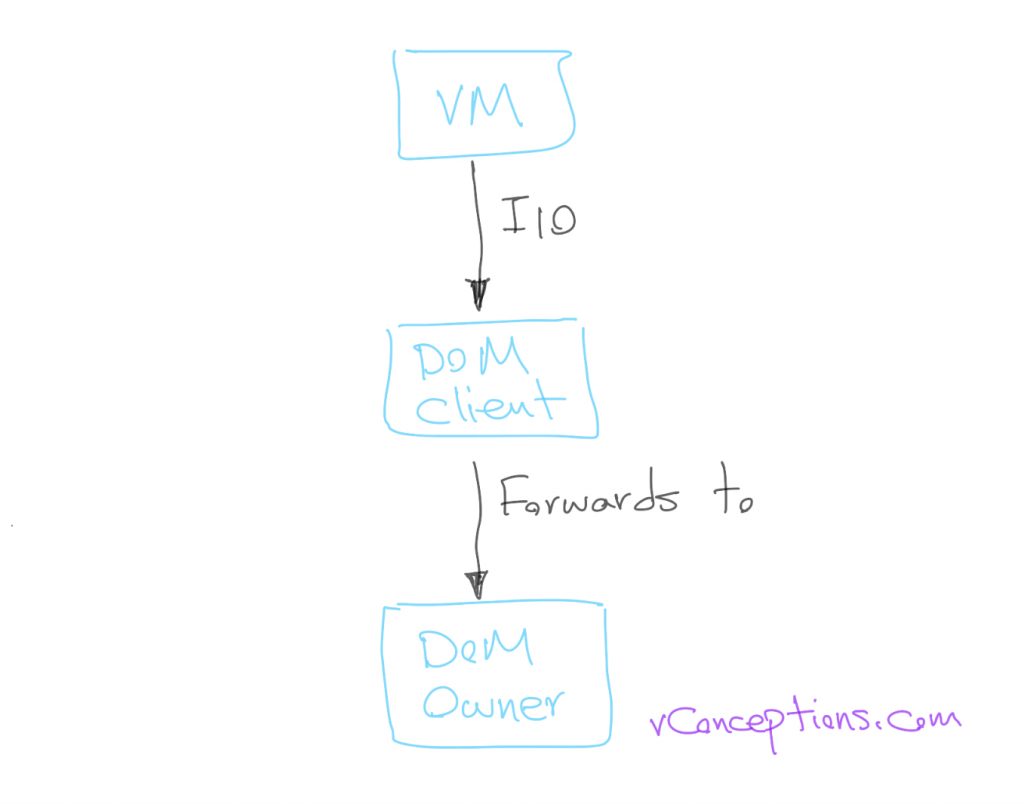
DOM Owner: Receives the forwarded I/O by DOM client and ensures object accessibility. It also replicates I/O based on object RAID levels. It determines in which components the data block resides. It forwards the I/O to DOM component manager.

DOM component Manager: Interacts with the LSOM locally to commit the I/O to the physical disk.
LSOM
LSOM as its name represents handles operations related to local physical disks including, creating components instructed by DOM and providing read caching and write buffering. It also provides the encryption process.
it interacts with the physical disks and reports unhealthy devices and performs I/O retries on failing devices. When a vSAN node boots up, it automatically tries to perform log recovery and LSOM is taking care of that.
CMMDS
CMMDS records some of the information such as owners of the objects and metadata information. it also defines master, backup and agent cluster roles.
RDT
Reliable Datagram Transport is a network protocol that carries vSAN traffic.
These were some of the internal components of vSAN and understanding them would help troubleshoot vSAN issue much better.